How Blockchain Is Transforming the Supply Chain Industry
1. Introduction to Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain
1.1 The Basics of Blockchain
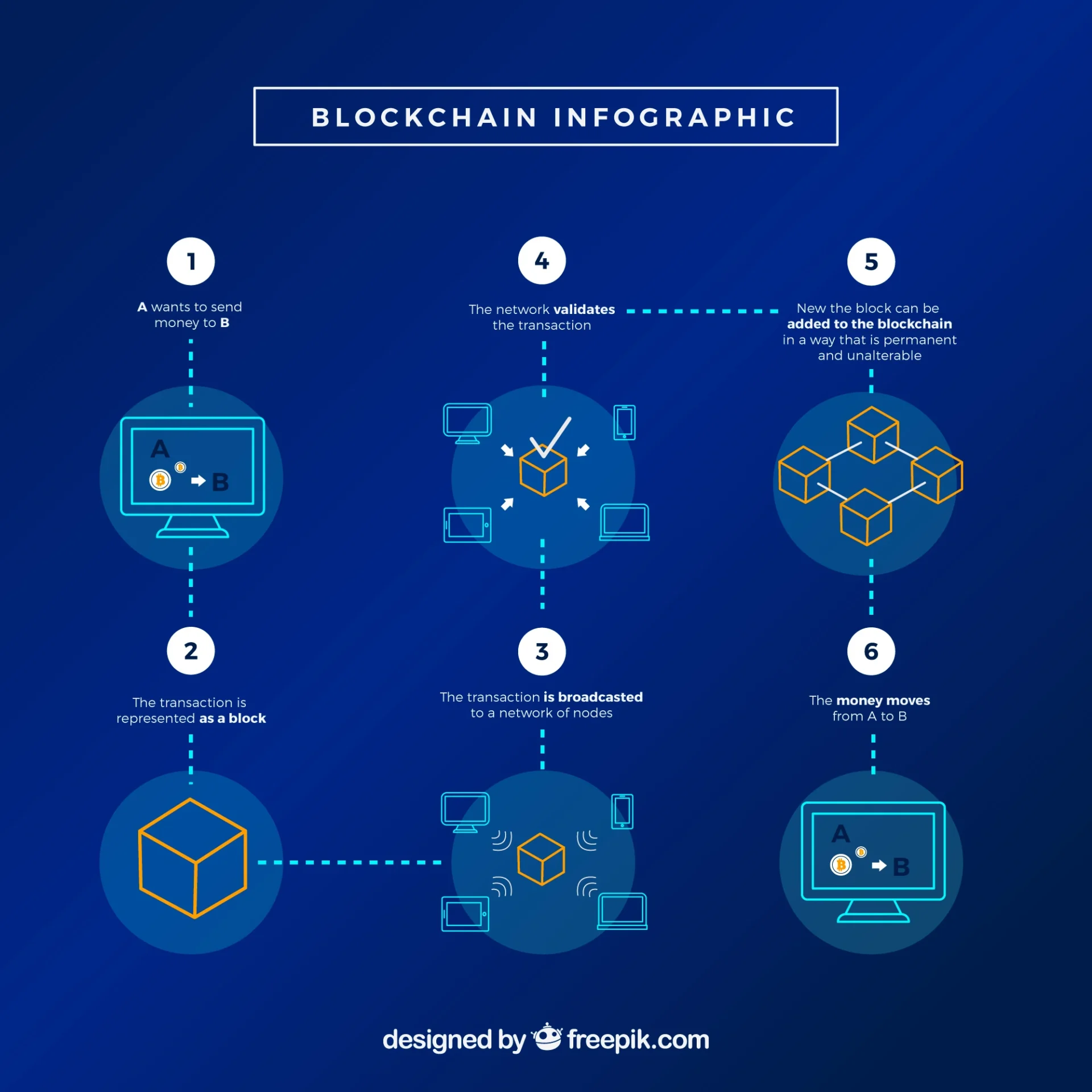
Blockchain is like a digital ledger that records transactions across a distributed network of computers. Each transaction is encrypted and added to a “block,” creating a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain. This technology ensures transparency, security, and decentralization.
1.2 Overview of Supply Chain Industry Challenges
The supply chain industry faces numerous challenges such as inefficiencies, lack of transparency, counterfeiting, and data security issues. Traditional systems often depend on paperwork and manual processes, leading to delays and errors in tracking goods and verifying their origins. By leveraging IT consulting, cloud computing, and software development, businesses can modernize their operations and reduce these risks.
2. Increased Transparency and Traceability

2.1 Real-time Tracking of Goods
Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods at every stage of the supply chain, transforming how IT consulting and IT services support logistics. Each product is assigned a unique digital identity that can be traced back to its source, enhancing transparency through data security and cloud computing.
2.2 Verification of Provenance
With blockchain, verifying the provenance of products becomes easier. By scanning a product’s QR code or barcode, consumers and businesses can access detailed information about its origin, manufacturing process, and authenticity, boosting trust and eliminating counterfeit products.
3. Enhanced Security and Data Integrity
3.1 Immutable Record-keeping
Blockchain ensures data security and integrity through its tamper-resistant nature. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a reliable and immutable record of all activities within the supply chain.
3.2 Protection Against Counterfeiting
Blockchain helps combat counterfeiting by creating a transparent and secure system for tracking products, supported by IT consulting and cybersecurity. By verifying the authenticity of goods through blockchain technology, businesses enhance data security and reduce the risk of counterfeit products entering the market.

4. Streamlined Efficiency and Automation
Smart Contracts for Automated Processes
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In the supply chain industry, smart contracts automate processes like payments, compliance checks, and product deliveries, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Reduction of Paperwork and Manual Tasks
Blockchain streamlines supply chain operations by digitizing and automating manual tasks, a major benefit recognized in IT consulting and software development. By eliminating paperwork, reducing human error, and increasing efficiency, blockchain technology supports more secure and transparent processes.
5. Impact on Inventory Management and Logistics
Optimization of Inventory Levels
Blockchain in the supply chain industry helps optimize inventory levels by providing real-time visibility into product movements and demand fluctuations. This level of transparency, supported by IT consulting, cloud computing, and data security, allows businesses to streamline inventory management processes.
Improvement in Supply Chain Visibility
Blockchain enhances supply chain visibility by creating a tamper-proof record of every transaction, from the manufacturer to the end consumer. This increased transparency allows for better tracking of products, faster dispute resolutions, and ultimately, a more reliable and efficient logistics network.
6. Potential Challenges and Adoption Barriers
Integration with Existing Systems
One of the main challenges in adopting blockchain technology in the supply chain is integrating it with existing systems. Legacy systems may not be compatible with blockchain platforms, requiring businesses to invest in software upgrades or custom solutions to ensure seamless integration.
Regulatory Compliance Concerns
Regulatory compliance is a significant adoption barrier for blockchain in the supply chain industry. Different regions enforce varying regulations around data privacy, security, and ownership rights, complicating implementation across jurisdictions. With support from IT consulting and cybersecurity services, businesses can navigate these challenges more effectively.
7. Case Studies of Successful Blockchain Implementation
Company A: Supply Chain Transparency Through Blockchain
Company A implemented blockchain technology to enhance transparency in its supply chain, leveraging IT consulting and software development to drive the transformation. By recording every transaction on a secure blockchain ledger, supported by data security and cloud computing, they were able to track products from origin to destination. This real-time visibility ensured product authenticity and significantly reduced the risk of counterfeit goods entering the market. With the help of managed IT services, IT support, and reliable IT solutions, Company A strengthened its supply chain operations and built greater trust with stakeholders.
Company B: Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains with Blockchain
Company B leveraged blockchain to achieve cost savings and efficiency gains in its supply chain operations. By automating processes, streamlining documentation, and enhancing trust among supply chain partners, they were able to reduce operational costs and improve overall productivity.
8. Future Trends and Opportunities in Blockchain Supply Chain Integration
Expansion of Blockchain Applications in Supply Chain
The future of blockchain in the supply chain industry is promising, with potential applications expanding beyond traditional tracking and authentication. Innovations such as smart contracts, IoT integration, and AI-powered analytics are poised to revolutionize supply chain management, offering new opportunities for efficiency and collaboration.
Potential for Industry-wide Adoption
As blockchain technology matures and standards for interoperability are established, the potential for industry-wide adoption in the supply chain continues to grow. With the support of IT consulting, software development, and managed IT services, businesses can overcome technical barriers and integrate blockchain more effectively. Collaboration among stakeholders, continued research, and regulatory support are crucial in driving widespread adoption of blockchain solutions, backed by strong data security and cloud computing. In conclusion, the integration of blockchain into supply chain operations marks a new era of trust, accountability, and productivity.